Estimating mathematical constants with Monte Carlo simulations
Marton Trencseni - Sun 09 October 2022 • Tagged with monte-carlo, simulation, math
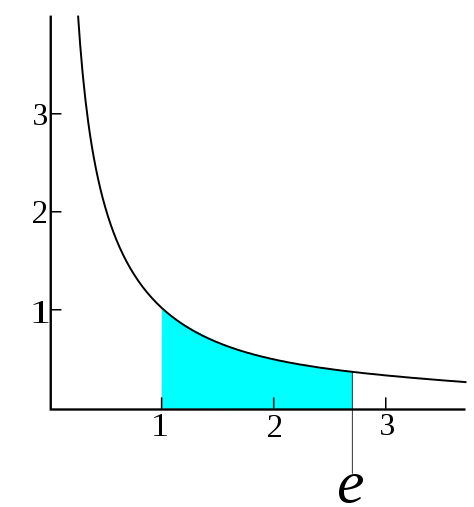
I use simple Monte Carlo simulations to estimate some mathematical constants: √2, ϕ, e and π.
Marton Trencseni - Sun 09 October 2022 • Tagged with monte-carlo, simulation, math
I use simple Monte Carlo simulations to estimate some mathematical constants: √2, ϕ, e and π.

Marton Trencseni - Sat 01 October 2022 • Tagged with interviewing
I will attempt to enumerate all the categories of questions commonly asked in technical interview loops, and my experience with them.

Marton Trencseni - Sat 24 September 2022 • Tagged with gpt, gpt-3
Here I will show a "conversation" with GPT-3 to gauge how good a particle physicist — or an illusion of a particle physicist — it is.

Marton Trencseni - Fri 23 September 2022 • Tagged with culture
I wrote a Culture Doc for the Data Science team I lead.

Marton Trencseni - Sat 03 September 2022 • Tagged with gpt, gpt-3
I have further "conversations" with GPT-3, this time asking more difficult questions about real-world Data Science projects I have personally worked on.

Marton Trencseni - Sun 31 July 2022 • Tagged with gpt, gpt-3
Recently I have been playing around with OpenAI's GPT-3 and I am very impressed by it. It reminds of the famous Arthur C. Clarke quote, “Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” Here I will show a "conversation" with GPT-3 to gauge how good a Data Scientist — or an illusion of a Data Scientist — it is.

Marton Trencseni - Sat 23 July 2022 • Tagged with book, typography
The Elements of Typographic Style by Robert Bringhurst is the most beautiful book I've ever held in my hand. This stunning piece of readable art shows Bringhurst's love for the craft of design, typography and writing, and his mastery of these subject, a result of his life-long devotion to them. I am not a professional typographer, but I enjoyed glancing at, reading and appreciating every page of this book.

Marton Trencseni - Fri 22 July 2022 • Tagged with book, management, culture
The Culture Map by Erin Meyer is a system of 8 scales which can be used to determine how cultures vary along a spectrum. The scales can be used to analyse one culture relative to another and decode how culture influences your international collaborations. I find the considerations in the book helpful irrespective of cultural background; the 8 scales can be applied to individuals as well, irrespective of where they are from.

Marton Trencseni - Sun 10 July 2022 • Tagged with amazon, book, management, writing
Amazon established a set of principles and mechanisms, enabling the company to grow from a single founder to several hundred thousand employees while remaining stubbornly true to its mission of obsessing over customers to create long-term shareholder value.

Marton Trencseni - Fri 08 July 2022 • Tagged with hbr, book, management, writing
If your writing is sloppy and artless people will think you are the same. They won’t care about your message, they won’t do business with you. It’s not true that only ideas matter. Good writing gets ideas noticed.

Marton Trencseni - Sat 18 June 2022 • Tagged with culture, facebook, netflix, valve
Many companies have some sort of "Culture Doc", a booklet or similar, which explains to new joiners what the company is about. I received Facebook's "Little Red Booklet" when I joined in 2016 February, and I was amazed how good it was. Recently I was researching other companies' Culture Docs, and found a version of Netflix's and Valve's online. It's interesting to compare and contrast what these different companies choose to put in their Culture Doc. Facebook's Culture Doc is very mission and execution oriented and serious, Netflix is analytical and HR-focused, and Valve's is a lighthearted explanation of how the company works.

In my experience, many Data Scientists struggle to write SQL queries in interviews.
Marton Trencseni - Sun 22 May 2022 • Tagged with python, decorators
I show toy implementations of Python decorator patterns that may be useful for Data Scientists.
Marton Trencseni - Thu 12 May 2022 • Tagged with python, dataclass, decorator
I write a toy implementation of Python's @dataclass decorator to improve my Python fu and learn more about decorators and metaprogramming.
Marton Trencseni - Sun 08 May 2022 • Tagged with python, decorators
I show toy implementations of Python decorator patterns such as @measure, @repeat, @trace, @count, @singleton, and @app.route (made famous by Flask).
Marton Trencseni - Thu 05 May 2022 • Tagged with python, enum
I extend my previous toy implementation of Python's Enum class to add more features.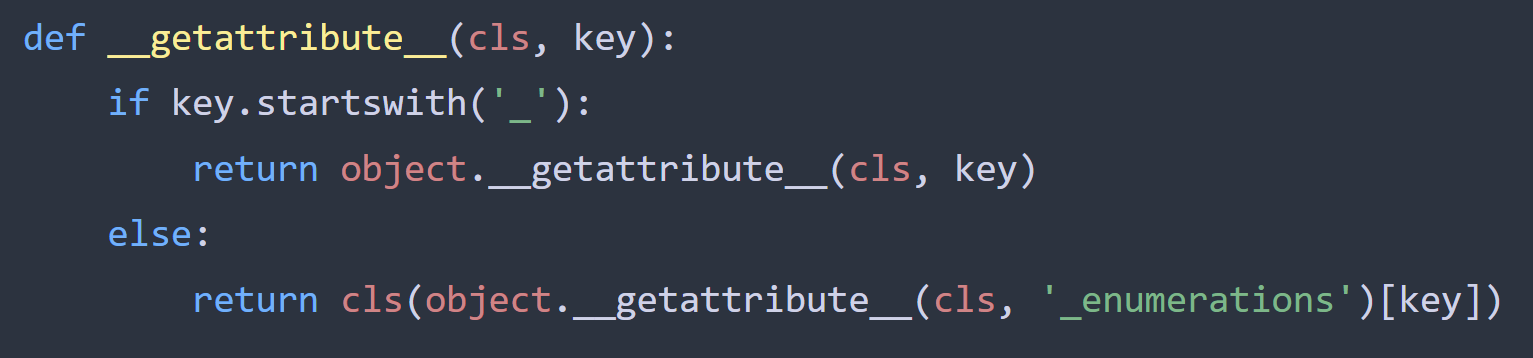
Marton Trencseni - Tue 03 May 2022 • Tagged with python, enum
I write a toy implementation of Python's Enum class to learn about Python metaclasses.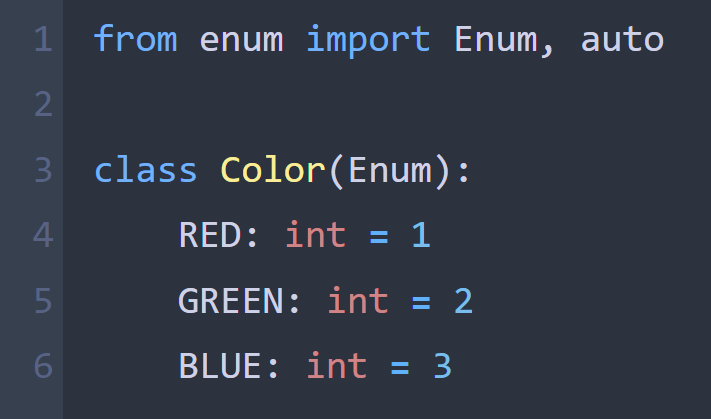
Marton Trencseni - Sat 30 April 2022 • Tagged with porsche, timeseries, fit, survival
Porsche proudly advertises "Over 70% of all Porsche vehicles ever built are still on the road today". Is this a testament of the quality and longevity of Porsche cars, or simply a result of the brand switching from niche sportscar manufacturing to mass production around the year 1999?

Marton Trencseni - Tue 26 April 2022 • Tagged with startups, theranos, wework, scalien
Theranos, WeWork and the startup hustle.

Marton Trencseni - Fri 22 April 2022 • Tagged with python, types
I show slightly more advanced aspects of type checking in Python for Data Scientists.
